Land shrimp farming: Save SE Asia’s mangroves, Boost tourism
If you travel to Japan, you may be surprised by how many dishes use shrimp. Japan is one of the world’s largest consumers of shrimp.
Shrimps or Prawns are a special part of Japanese food culture. Of course, shrimps are delicious. But there are also 3 symbolic factors behind the Japanese people’s deep love of eating them.

- A symbol of long-life
People said that its long beard (antennae) and bent back resemble the elderly. - A symbol of joy (festivity)
Shrimps have protruding eyeballs and turn bright red when boiled, making them a symbol of celebration. - A symbol of good luck
Shrimps are a symbol of great luck because they have mighty jumping power.
90% of the shrimps available in Japan today rely on imported frozen products from Vietnam, India, Indonesia and others. The domestic food self-sufficiency rate is only 10%.
Black tiger shrimp used to dominate the imports. Around 2003, Whiteleg Shrimp, a species originating from Central and South America, replaced it. This is due to a virus infecting the shrimp. Today, 70-80% of the world’s shrimp farming market belongs to whiteleg shrimp.
The whiteleg shrimp rarely hide in the sand bottom and tend to swim actively in the water. In other words, the production is more efficient because it can cultivate in three dimensions. This is also one of the reasons for its widespread use.
In recent years, Japan has put much effort into “land-based aquaculture” of whiteleg shrimps. Yes, Japan aims to produce a domestic cultivated shrimp that is also delicious as sashimi.
And what is behind all this is some of Japan’s social structures and its efforts to achieve sustainability.
・Japan has the world’s most severe low birthrate and ageing population. As a result, more and more farmlands are now inactive in the mountains as young people flock to urban areas.
・Fishing harvests in Japan’s coastal waters are decreasing.
・Conventional aquaculture facilities in Southeast Asia and other countries place a heavy burden on the surrounding natural environment. It has led to massive damage to the natural environment.
In land-based shrimp farming, people dig the ground and use impermeable sheets to create large ponds as aquaculture water tanks. What is crucial to the system is the seawater recirculate in the septic tanks. The system is sustainable as it can keep using the seawater even after its first use. Such water purification systems are a field where Japanese companies excel with some of the best technology in the world.
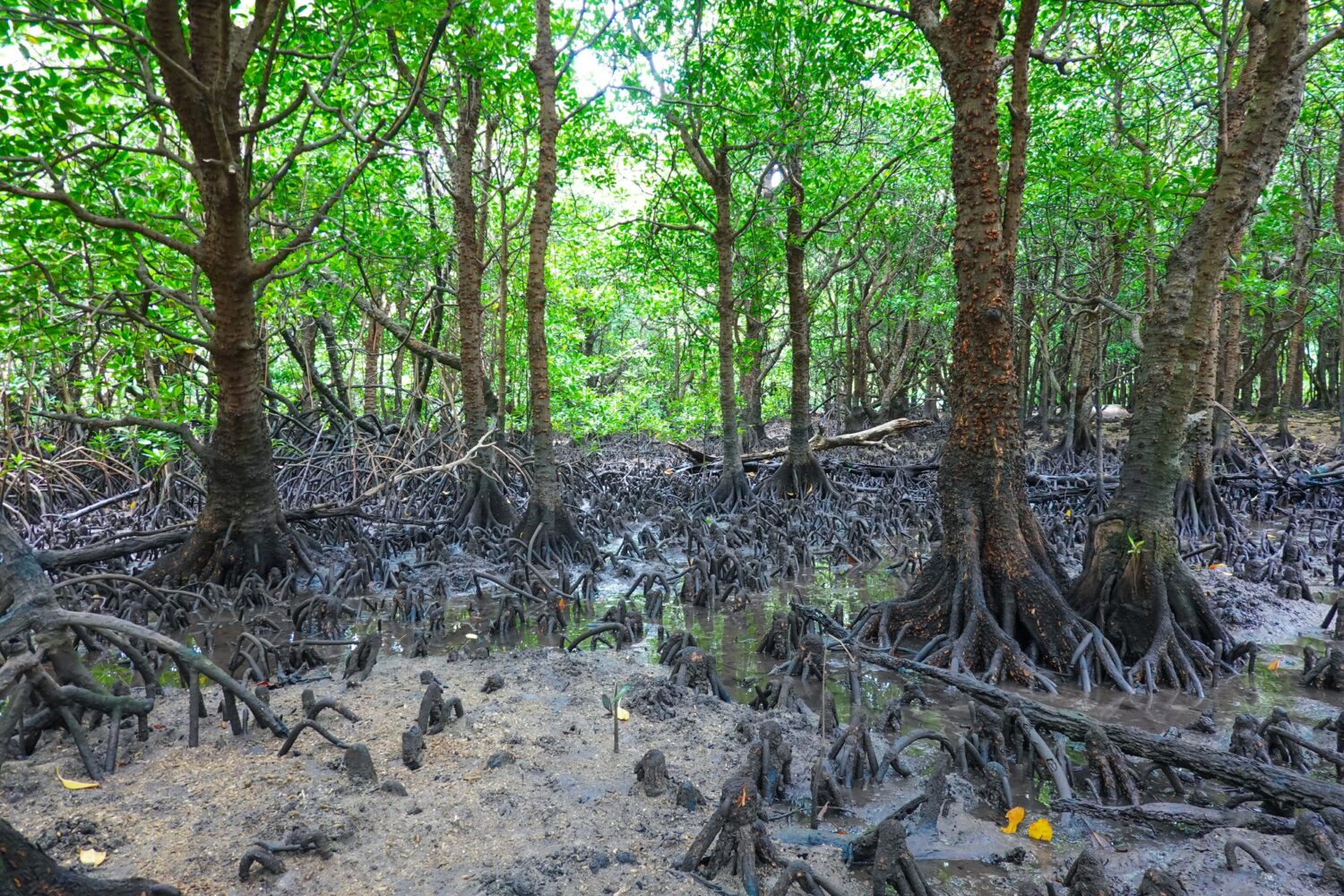

A common style of shrimp farming around the world is draining water. The system constantly uses water from outside the farm, then releases the water back to the environment through the aquaculture area. Shrimp farm development puts a great burden on the environment. Shrimp are bred under overcrowding to achieve production efficiency. They eat a large amount of food, which pollutes the farm. Polluted water released from the farms kills mangrove forests.
Polluted farms are then abandoned, building new ones in new areas. Thus, destroying mangrove forests by this process. In Thailand, mangrove forests decreased by half over the past 40 years.
On the other hand, land-based aquaculture blocks any interaction with the external environment, so the risk of viral infection is significantly low. Unlike imported shrimps which so far cannot be eaten raw, this farming system will allow the supply of shrimps suitable for sashimi and sushi.
In Japan, tourist destinations are expecting to use shrimps grown in land-based aquaculture as a tourist resource. For example, by creating new kinds of food menus.
We have a network of Japanese companies keen to expand into the Halal market in Malaysia & Indonesia.
If you are interested in connecting with sustainable technology companies in Japan, simply JOIN the network from below. We will match the right one for you!